How to Setup A Redundant RPC Service in RabbitMQ
What is an RPC Service?
An RPC Service is a messaging pattern to implement a request/response style communication. An RPC Client sends a request message to a Request Message Queue that is ultimately consumed by a RPC Service. This RPC Service must send back a response message to a message queue that is created by the RPC Client before it published the request message into the request message queue. The response message queue is normally an unnamed or anonymous queue whose queue name is passed along with the request message inside the “reply-to” message property field. The RPC Service use the name of that queue that is passed inside the reply-to property to determine which queue to publish the response message to.
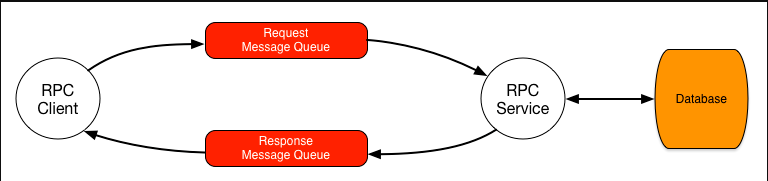
In the above setup, if the RPC Service becomes unavailable, then the whole system will stop working. Fortunately, RabbitMQ makes it very easy to add another RPC Service to create a redundant system.
How to Setup Redundant RPC Service
By running another instance of the same RPC Service (depicted in green in the diagram below), we can create a redundant RPC service.
There are few things to consider:
- Both RPC Service instances must be stateless. This means that the state must be stored and shared in common storage such as a database.
- Both RPC Service instance must be binded to the same Request Message Queue. This is not the same as both RPC Service using its own message queue.
- This system should be configured with round-robin dispatch in order to distribute the workload onto multiple RPC Services.
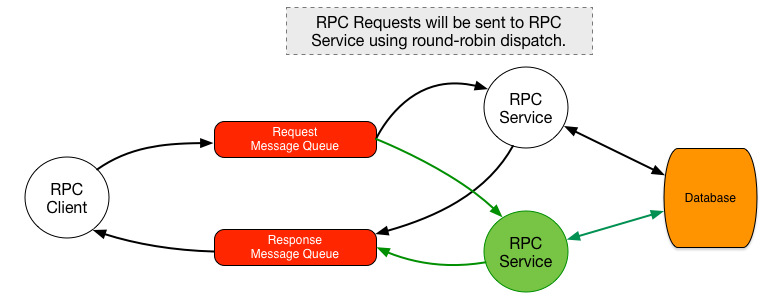
One of the additional benefits of using RabbitMQ to implement redundant RPC services, is that you can scale out with multiple RPC Services across multiple processes and machines.
Conclusion
In order to create scalable RPC Services in RabbitMQ you need to follow specific guidelines highlighted above. When done correctly, using RabbitMQ can create both a redundant and scalable system.